Ovale has dormant liver stages hypnozoites that can activate and invade the blood relapse several months or years after the infecting mosquito bite. Heterozygote advantages are particularly fascinating because they can.

Annual Parasite Incidence Malaria Cases 1000 Population In India For Download Scientific Diagram
Multiple phenotypes survive in a balanced polymorphism The usage of the insecticide DDT to control mosquitoes resulted in directional selection to insecticide resistance in the insects.

. Organic Compounds 4 Organization Of The Cell 5 Biological Membranes 6 Cell Communication 7 Energy And. Temperature is particularly critical. Human malaria is one of the most ubiquitous and prevalent human infectious diseases around the world.
Malaria is an acute febrile illness caused by Plasmodium parasites which are spread to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The Chemical Basis Of Life 3 The Chemistry Of Life. From the point of view of public health it is important that in malaria-endemic countries patients with SCA and particularly children be protected from malaria by appropriate prophylaxis.
1 A View Of Life 2 Atoms And Molecules. People move for a number of reasons including environmental deterioration economic necessity conflicts and natural disasters. They found a high concentration of co-occurring mutations in neighboring genes that are inherited together with the MHC genes that happen to be associated with complex heritable disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimers several cancers and common autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Malaria is the evolutionary driving force behind sickle-cell disease thalassemia glucose-6. When malarias effect on child mortality is consideredand it was probably even greater before antimalarial drugs and other control measures were introducedit is not surprising that malaria is the strongest known selective pressure in the recent history of the human genome. Because of the population densities especially in Asia it is probably the most prevalent human malaria parasite.
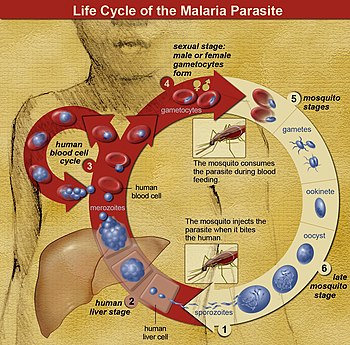
This explains why the gene for sickle cell anemia is found in about 7 of the population in malaria-stricken regions but is virtually nonexistent elsewhere. Infected mosquitos carry the disease transmitting it to humans through a bite. Falciparum is the deadliest malaria parasite.
Human migration causes this gene to be found in populations all over the world. Eldra Solomon Charles Martin Diana W. Scientists believe the sickle cell gene appeared and disappeared in the population several times but became permanently established after a particularly.
Plasmodiidae and vectored by mosquitoes in the genus Anopheles Diptera. Natural selection may not have had time to. These factors are most likely to affect the poor many of whom live in or near malarious areas.
For example at temperatures below 20C 68F Plasmodium falciparum which causes severe malaria cannot complete its growth cycle in the Anopheles mosquito and thus cannot be transmitted. To evade the human immune system and enter red blood cells a normally active gene in the malaria parasite nucleus goes into silent statethen switches back to active state when immunity wanes. Human migration causes this gene to be found in populations all over the world.
Human malaria includes the species Plasmodium falciparum P. Being heterozygous Ss is a superior adaptation in areas where malaria is endemic Heterozygote superiority is a major reason why genetic diseases persist in the human population Many mutations of blood proteins work in a similar fashion to stop the malarial parasite in its tracks. Too few humans have died of malaria to end.
In addition in SCA there is often hyposplenism which reduces clearance of parasites. December 13 2012 In order to spread disease inside the human body the malaria parasite must evade the. Culicidae 1.
For example a genetic variance causing sickle cell anemia actually protects against another disease malaria. Every year an average of 300 million people are diagnosed with the disease and on average around 500000 of those patients die. Humans are protected from the malaria parasite.
In the same virtual lab a model that explains this relationship is included. Why does the malaria disease persist in the human population. This acute febrile illness is caused by protozoan intracellular obligate parasites in the genus Plasmodium Haemosporida.
The conditions required by the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are commonly found in nature. Why Malaria Persists Throughout the course of history there has never been a deadlier disease than malaria. One of the factors contributing to the reemergence of malaria is human migration.
There are 5 parasite species that cause malaria in humans and 2 of these species P. It occurs when an allele which is undesirable in its homozygous form gives the organism an advantage in its heterozygous form. Normally monocytes form the immune systems first line of defense against foreign invasion sensing danger from afar and alerting other immune mechanisms to mount an effective response.
Vivax as well as P. Vivax pose the greatest threat. Why does malaria persist in the human population.
Malaria is caused by organisms of the genus Plasmodium a protist that infects human red blood cells. Heterozygote advantage maintains both the normal allele and the sickle cell allele in the population. The simplest explanation of this fact is that malaria makes the anaemia of SCA more severe.
Malaria parasites can complete their growth cycle in the mosquitoes extrinsic incubation period. Malaria parasite transforms itself to hide from human immune system. However in many parts of the world the gene that causes sickle cell anemia is more common because a single copy of it confers resistance to malaria.
Natural selection may not have had time to. However in many parts of the world the gene that causes sickle cell anemia is more common because a single copy of it confers resistance to malaria.

Global Prevalence Of Malaria According To Who 17 Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments